Ten Things You Didn’t Know Git And GitHub Could Do
Git and GitHub are powerful tools. Even if you have worked with them for a long time, it’s likely that you haven’t stumbled across everything yet. I collect 10 common tricks for both Git and GitHub that potentially increase your day-to-day productivity.
GitHub
keyboard shortcut: t & w
On your source code browsing page, press t to enter the fuzzy file finder mode:
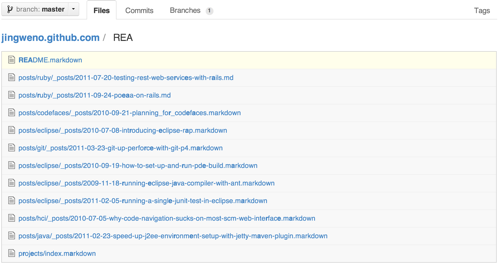
On your repository’s home page, press w to quickly filter branches:
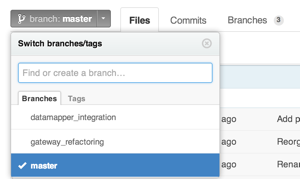
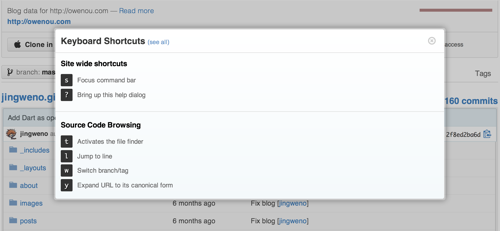
On any GitHub page, press ? to show the list of shortcuts applied to a particular page:
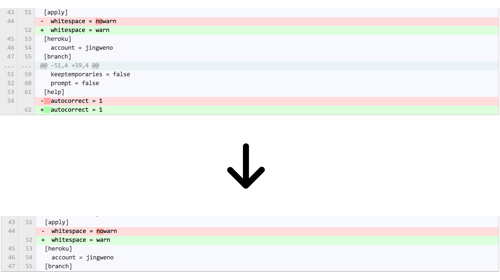
ignoring whitespace: ?w=1
Add ?w=1 any diff URL to trim whitespace:
commits by range: master@{time}..master
You can create a compare view in GitHub by using the URL github.com/user/repo/compare/{range}. Range can be two SHAs like sha1…sha2 or two branches’ name like master…my-branch. Range is also smart enough to take time into consideration. For example, you can filter a list of commits since yesterday by using format like master@{1.day.ago}…master. The link https://github.com/rails/rails/compare/master@{1.day.ago}…master, for example, gets all commits since yesterday for the Rails project:

commits by author: ?author=github_handle
You can filter commits by author in the commit view by appending param ?author=github_handle. For exmaple, the link https://github.com/dynjs/dynjs/commits/master?author=owenthereal shows a list of my commits to the Dynjs project:
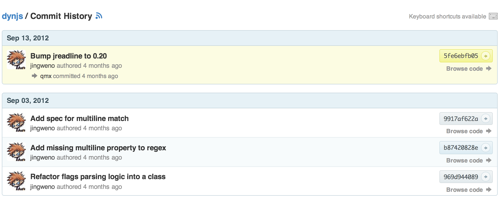
.diff & .patch
Add .diff or .patch to the URLs of compare view, pull request or commit page to get the diff or patch in text format. For example, the link https://github.com/rails/rails/compare/master@{1.day.ago}…master.patch gets the patch for all the commits since yesterday in the Rails project:

email reply
You can comment directly by replying to the email received from GitHub instead of commenting on the website. GitHub will route your reply correctly:

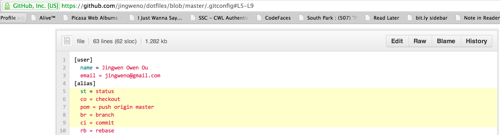
line linking
In any file view, when you click one line or multiple lines by pressing SHIFT, the URL will change to reflect your selections. This is very handy for sharing the link to a chunk of code with your teammates:
subscribing peoples
Mentioning users in pull requests, issues or any comment will subscribe them to all subsequent notifications:
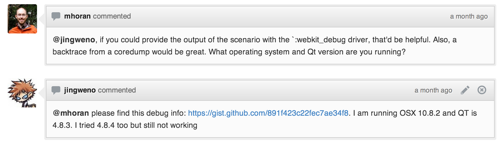
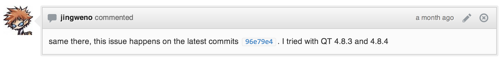
autolink
In pull requests, issues or any comment, sha and issue number (#1 for example) will be automatically linked. Besides, you can link sha or issue number from another repository with the format of user/repo@sha1 or user/repo#1 respectively. The following is an example of autolinking a sha in a comment:
hub
Hub is the command line GitHub. It provides integration between Git and GitHub in command line. One of the most useful commands is creating pull request by just typing “hub pull-request” in your terminal. Detail of all other commands is available on its project readme.
Git
git log -p FILE
To view changes in history for README.md, for example, type
> git log -p README.md
git log -S’PATTERN’
To search for changes that matches the pattern “stupid” in history, for example, type
> git log -S'stupid'
Combining with “-p” shows the changes with the search pattern.
git add -p
To interactively stage and unstage changes, type
> git add -p
Updated 2013-01-18: From @tjwallace, git checkout and git reset also support the –patch (-p) option for the interactive mode.
Updated 2013-03-17: From jasherai, git stash also supports the –patch (-p) option.
git rm –cached FILE
This command removes remote file copy only. For example, typing
> git rm --cached database.yml
removes database.yml that is already checked in but leaving the local copy untouched. This is intensively handy for removing ignored files that are already pushed without removing the local copies.
git log ..BRANCH
This command returns all the commits in a branch that are not in HEAD. For example, assuming you are on a feature branch, typing
> git log ..master
gets all commits that are in master but not merged into the current feature branch yet.
git branch –merged & git branch –no-merged
This command returns a list of branches that are merged or not yet merged to current branch. It’s a useful check before any merging happens. For example, on a featrue branch, typing
> git branch --no-merged
returns a list of branchs that are not yet merged to the feature branch.
git branch –contains SHA
This returns which branch contains a specified sha key, for example, typing
> git branch --contains 2f8e2b
shows all branches containing the commit 2f832b. It is very helpful for verifying whether a git cherry-pick is done correctly for instance.
git status -s
It returns a less verbose version of git status. I setup this command as my default when running git status to reduce noise.
git reflog
It shows a list of operations you have done to your local git repository. It’s very helpful for restoring lost commits for example since it returns the complete history of all git operations with commit SHAs.
git shortlog -sn
This shows a list of contributors ordered by number of commits. Similar to the contributors view of GitHub.
Summary
Git is a well engineered tool. Understanding it will definitely make you a more productive and capable programmer. GitHub, on the other hand, provides handy team collaboration features on top of Git. Being able to use GitHub well also increases your day-to-day efficiency.
To further deepen your Git and GitHub skills, I recommend the following materials:
- ProGit, the best book on Git
- Advanced Git serials by Peepcode
- Git and GitHub Secrets talk by Zach Holman
